In modern businesses, GRC is essential for upgrading the existing compliance practice. Thus, GRC meaning signifies governance, risk, and compliance which manage risks. The GRC audit helps to optimize the processes and controls of industry-specific regulations. Therefore, applying GRC auditing puts you at the top of security and compliance practices. The process allows you to recognize gaps in security postures and prevent breaches. In brief, executing a GRC audit will help your organization optimize its GRC program and ensure it meets the relevant security requirements.
This article explores the GRC meaning with the audit process. It covers the fundamental ideas about auditing and best practices. Read the article for more precise information about GRC meaning.
UNDERSTANDING GRC AUDIT
GRC is an organization’s internal approach to securing compliance. The audit process overviews the organization’s policies and processes for complying with compliance. In addition, it assesses the implementation of the GRC framework, identifies security vulnerabilities, and addresses insufficiencies in the existing process. Thus, each organization has unique GRC audit deliverables and processes. Moreover, audits can be segregated into internal and external audits. An internal audit improves the controls and procedures of compliance practice, whereas an external audit offers certification or a compliance report.
Internal vs. External Audits
An internal audit signifies that an internal team will assess the efficacy of the GRC program in protecting the businesses and finding areas of weaknesses. Meanwhile, the third-party auditor performs an external audit to help the stakeholders understand the GRC program and assure them about your business’s security and safety measures.
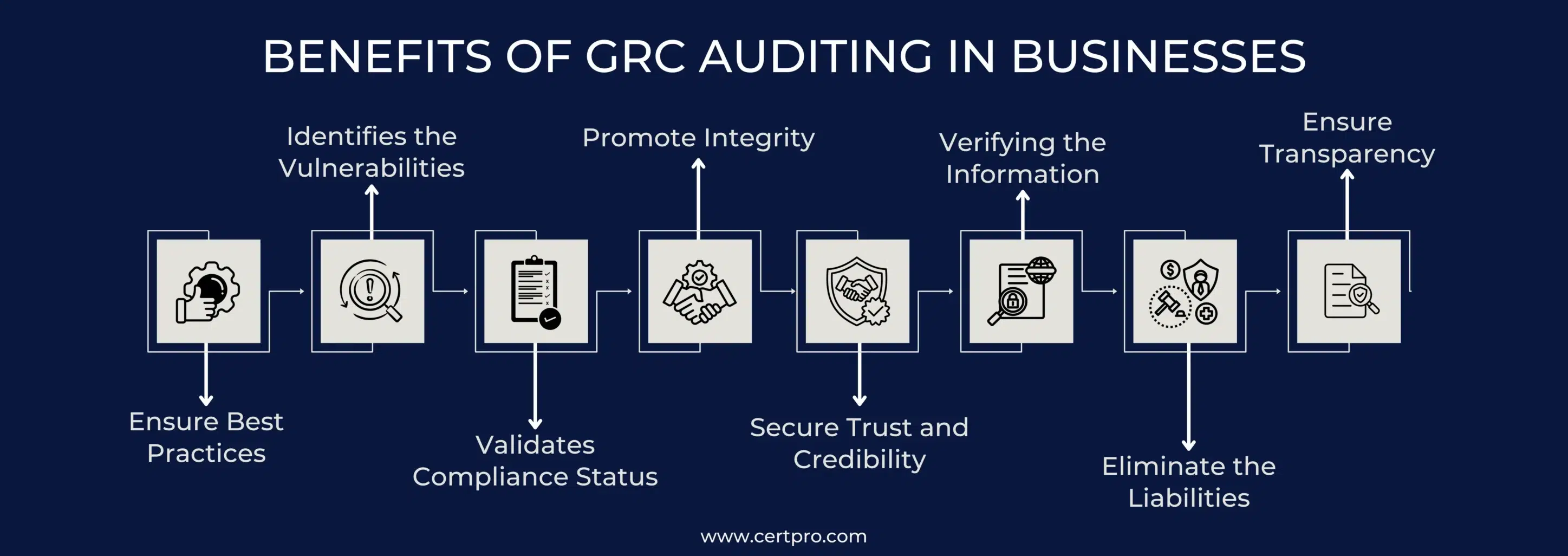
BENEFITS OF GRC AUDITING IN BUSINESSES
GRC meaning your organization applying a GRC program to optimize and enhance the compliance practice. The GRC auditing confirms the continuity of the program and has some other benefits:
Ensure Best Practices: The auditing verifies the ethical, accountable, and transparent use of controls to comply with the regulations.
Identifies the Vulnerabilities: It assesses the potential gaps in the existing controls and responds to the business risks. Thus, it eliminates the risk of breaches in the process.
Validates Compliance Status: The auditing confirms that policies and controls are well-placed to adhere to compliance.
Promote Integrity: The audit process supports alignment between the organization’s activities and core values, thus promoting integrity.
Secure Trust and Credibility: Auditing denotes the organization’s seriousness about compliance practices. Therefore, it helps develop trust and business relationships within the market.
Verifying the Information: The audit process validates an organization’s secure practice and assures the board members and investors about the safe practice.
Eliminate the Liabilities: The primary benefit of auditing is that it eliminates the risk of financial, legal, and reputational damages. Therefore, GRC meaning denotes business continuity and growth.
Ensure Transparency: The audit process most prominently ensures your organization’s transparency and accountability in terms of functionality.
STEPS OF GRC AUDITING FOR YOUR BUSINESSES
The four fundamental components can help your organization execute a compact internal GRC audit process. Let’s discuss the components in detail:
Planning: It is essential to plan the audit and outline the scope of the process. In your organization’s case, an audit committee will be developed, and the committee will decide which departments and employees will actively participate in the process. Thus, incorporating a maximum number of people will provide more satisfying feedback and results. In this regard, the internal auditing team must have a deadline to complete the audit process and submit the report.
Fieldwork: In this segment, your organization’s auditors will directly talk to the stakeholders and employees to recognize the success of the business process. This helps to identify non-compliance and vulnerabilities in the process. Therefore, the organization must rectify the flaws discovered in the GRC audit process. Hence, GRC meaning a robust security framework that eliminates the risk of error.
Audit Report: The auditor gathers information that offers meaningful insights into your organization’s status. Therefore, the audit reports signify the vulnerabilities and errors in the process, and the auditor suggests the appropriate measures for the flaws. Thus, GRC meaning the elimination of insufficiency in the process and ensuring compact security practices.
Follow-up: The result of a GRC audit is a report. After the auditing is completed, your organization can get two kinds of results: non-conformity results and observation results. Thus, non-conformity results identify gaps and discrepancies in the process. It points out the gaps between what the organization outlines and what occurs. On the other hand, observation results suggest alternative security measures for the betterment of the whole process. The follow-up process helps your organization confirm the concerns are resolved and new threats are identified.
BEST PRACTICES FOR SUCCESSFULLY AUDITING GRC PROGRAMS
A successful GRC audit will depend on the following points:
Scope of Audit: The GRC framework depends on the organization’s complexity and structure. Similarly, the audit process will be unique and rely on the system controls and databases assessed by your company.
Set an Audit Plan: Before starting the audit, it is essential to create a plan. A compact plan can help you achieve the goal and inform the stakeholders about the exact process of the audit.
Conduct Risk Assessment: A practical risk assessment helps you identify potential risks that could arise in your audit and take steps to mitigate them for functional continuity.
Analyze the GRC Component: In these steps, your team will audit all the GRC components and document the controls you have in place. Again, whenever possible, review the controls to understand their effectiveness.
Report the Findings: Report your findings, including all reviewed GRC controls and practices. The report must identify areas for improvement and vulnerabilities.
Create an Action Plan: The audit report finds the immediate gaps. The organization must address these issues by taking appropriate measures.
HOW TO USE GRC TOOLS IN THE AUDIT PROCESS
GRC auditing evaluates an organization’s implementation of GRC processes relative to a specific GRC framework. In detail, an audit may include evidence collected on the GRC controls implemented across the organization. The audit also examines the security controls required to manage cybersecurity risks and reviews department-specific compliance with regulatory frameworks. The specific requirements of GRC frameworks depend on your particular governance, risk management, and compliance needs. Thus, auditing is critical to assessing the effectiveness of your organization’s GRC processes.
GRC meaning the application of tools to improve the effectiveness of the audit process. Thus, GRC software can streamline the audit process by simplifying evidence collection. The tools allow you to collect evidence from various assets of your organization. In addition, the tools govern the audit process and match the compliance requirements of the regulatory framework. Therefore, GRC internal audit software simplifies GRC management and streamlines your organization’s GRC program.
CHALLENGES ASSOCIATED WITH GRC AUDITING
The implementation of GRC is a complex process, along with the auditing. Therefore, organizations can face multiple challenges when applying GRC audits. Some of them are listed below:
Complexity of Regulations: Regulations are evolving to mitigate the threats. Similarly, the requirements and enforcement techniques also change with the rules. Thus, compliance practice becomes daunting and challenging with time.
Diverse Risks: The globalization of businesses increases the risk of cyber threats, geopolitical risks, supply-chain disruptions, fraud, and corruption. Thus, auditing has become more challenging than ever.
Miscommunication: Cooperation and collaboration are essential for GRC auditing. Thus, any miscommunication within the organization can affect the audit process.
Resource Constraints: GRC meaning a compact process that ensures security for your organization. However, the audit process requires financial and human support, which creates resource challenges in the GRC program.
Lack of Agility: Business environments change with time. Risk and regulations evolve to prevent new threats to businesses. Thus, organizations need to improve their capabilities to adjust to new changes.
CLOSING THOUGHTS
GRC meaning a compact process that helps your organization maintain compliance. Therefore, performing a GRC audit enables you to understand the control’s effectiveness and find flaws. Similarly, an effective audit process demands effective planning, testing, and transparent reporting. Thus, you can simplify the process with effective GRC software that gathers evidence and helps organizations conduct more impactful auditing processes. Moreover, optimizing audits enables you to maximize the effectiveness of your GRC program.
Furthermore, a comprehensive audit and compliance automation helps your organization streamline compliance and strengthen your auditing process. Hence, you can seek help from GRC service providers to enhance the controls you implement across the program and promptly identify vulnerabilities in the GRC program.
FAQ
How often do you perform a GRC audit?
GRC audits are not fixed for all organizations. Depending on your company’s needs, it can be done once a year or regularly.
What is the GRC tool?
Governance, risk, and compliance (GRC) is an organizational strategy for managing risks while maintaining compliance. Businesses can use GRC tools to manage policies, assess risk, control user access, and streamline compliance processes.
What is the responsibility of GRC?
The GRC strategy integrates the correct policies and practices into the organization’s operations. It also ensures adherence to compliance practices and eliminates the risk of penalties.
What is the GRC principle?
Governance, Risk, and Compliance are the three parts of GRC. These three principles help companies reach their goals, handle risk, deal with uncertainty, and do the right thing.
How do I choose a GRC tool?
To select the correct tools, identify the goals and requirements, compare tools on the market, and evaluate the cost. Therefore, select the appropriate tools for your organization.

About the Author
Shivaprasad Shetty
Shivaprasad Shetty is an ISMS Lead Auditor and Consultant, adept at developing, implementing, and auditing ISO 27001-compliant frameworks. He is also well-versed in SOC 2 compliance, GDPR, HIPAA, and ISO 42001 standards. Shivaprasad excels in ensuring compliance across regulatory frameworks and fostering a secure organizational culture.
NAVIGATING DATA PRIVACY FRAMEWORKS: A COMPREHENSIVE GUIDE
Globalization has intense effects on business functioning and scaling. In today's digital world, companies are generating an unprecedented rate of data that requires protection from emerging cyber threats. In addition, recurring data breaches and privacy concerns make...
BUSINESS NON-COMPLIANCE: THE HIDDEN FINANCIAL AND OPERATIONAL COSTS
Businesses are always in a dilemma regarding whether or not to be compliant. Most companies think that compliance will problematize their operating process. However, highly regulated industries like financial and healthcare services meet the legal obligations for...
Security Frameworks: A Comprehensive Guide with 14 Examples
Technological advancements make cyberattacks more sophisticated and advanced. Hence, organizations must keep up with the latest cybersecurity frameworks in these complicated scenarios to sustain themselves in a dynamic threat environment. Different cybersecurity...