Modern society uses technology to make life simple and comfortable. Similarly, AI is introduced to make remarkable changes in human life. AI is now transforming industries from healthcare to entertainment, education to transport. Again, streaming services use AI to suggest playlists and create personalized content. In our daily lives, AI-powered digital assistance sets reminders and manages our needs. Thus, AI is a part of our lives that cannot be neglected. However, technological advancement has enormous benefits with few restrictions. Likewise, AI needs surveillance and robust management systems to improve its capabilities and eliminate errors.
In response to this urge, the European Union developed an Artificial Intelligence Act (EU AI Act) to create a regulatory framework for using AI. The Act targets organizations whose AI products are used in the European Union. Thus, the Act is concerned about using AI in the European Union. In the meantime, ISO developed an AI management system through the development of ISO/IEC 42001. It provides a valuable framework that helps navigate the EU AI Act requirements. ISO 42001 is an international standard for organizations using and deploying AI. Therefore, implementing the framework can reduce the risk of AI and help to grow your business in the European Union.
This blog will explore how ISO/IEC 42001 compliance supports you to align with the EU AI Act. What are the pointers where both frameworks overlap and diverge? In addition, the blog also touches on the basic concept of AI management and recognizes the impact of AI management regulations in the future.
EU AI ACT
The Act was adopted by the European Parliament in March 2024 and is expected to become mandatory in 2025. The EU AI Act is the first legal framework on AI that is concerned with AI’s risk in the European market. The Act aims to reduce the burden of AI while respecting the fundamental rights of the consumer. Thus, the Act is concerned with customer safety and the ethical use of AI. Hence, the basic principles of the AI Act include:
Human-Centric Approach: The Act puts customers at the center of AI development and use. Thus, it emphasizes using AI to serve people’s and society’s best interests.
Transparency: Transparency is paramount for building trust in AI uses. The AI Act aims to make the system transparent in the operational process. Thus, users must know they are interacting with an AI system and understand how it works.
Accountability: It is another crucial aspect when errors occur with AI systems, and there should be someone to take responsibility. Thus, the EU AI Act emphasizes provider accountability in the use of AI. In case of any mishap with AI systems, the organizations developing and deploying the AI systems will be responsible.
Safety and Security: The Act ensures that AI systems are safe and secure for users and communities. Additionally, it also confirms data security, risk management, and cybersecurity in AI use.
Data Governance: Data is the primary fuel for industries and AI systems. The Act ensures that the trained data are free from discrimination and biases. Thus, it protects personal data from cyber threats.
ISO/IEC 42001
ISO/IEC 42001 is the first international management system standard for AI. The certification process ensures that organizations have a robust framework for AI monitoring. In addition, the standard confirms that the organization is implementing a solid framework in AI management systems that requires continuous monitoring and improvement. Furthermore, the standard promotes the development of trustworthy and accountable AI. It encourages organizations to prioritize human well-being and assists organizations in complying with relevant laws. The key features of ISO 42001 include:
Transparency: The AI decision must be transparent and free from bias and discrimination. Hence, the users should get an effective solution from the AI systems.
Accountability: It helps in developing user trust. The organization must be responsible for AI-related decisions and consequences.
Fairness: AI is widely used in automated decision-making processes. Thus, the standard ensures fairness in the process.
Explainability: Explanations of crucial aspects impacting AI system outcomes should be presented to interested parties in an understandable format.
Data privacy: A comprehensive data management and security solution is essential for ensuring user privacy in an AI environment.
Reliability: AI systems must exhibit high safety and dependability in all areas
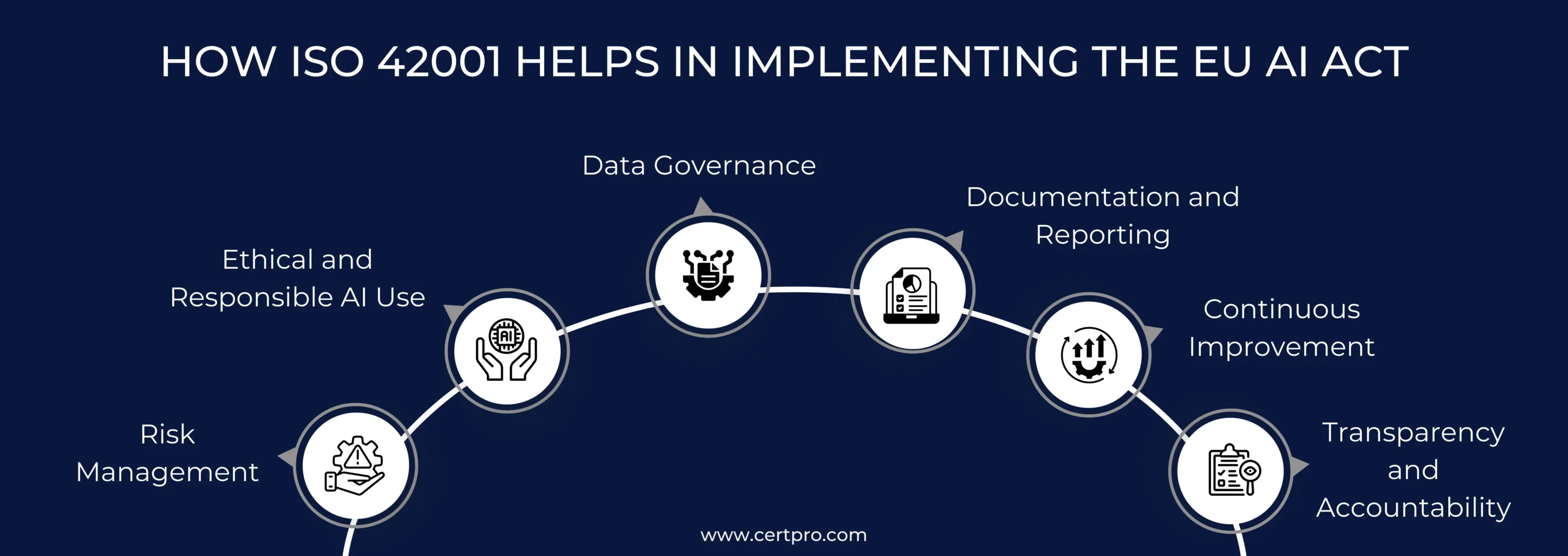
HOW ISO 42001 HELPS IN IMPLEMENTING THE EU AI ACT
The obligations under the AI Act fall on providers of high-risk AI systems in the EU member states. However, the impact of the law’s reach beyond the European borders. Organizations outside the EU that develop high-risk AI products used within the European Union will also come under the Act. Therefore, non-EU organizations also require AI regulations if their products or services are related to the EU market. Thus, following an AI management framework can benefit your organization in the long run. In this regard, ISO/IEC 42001 compliance supports the effort to align with the EU AI Act.
However, ISO/IEC 42001 compliance does not signify that the organization that follows ISO 42001 can comply with the EU AI Act. In some areas, the requirements of ISO 42001 and the EU AI Act overlap, and some places have unique criteria. Therefore, organizations must analyze and recognize the gap between the Act and its standards. In this context, you can get help from experts familiar with both the regulations. Here are some of the ways ISO/IEC 42001 compliance helps in navigating the EU AI Act:
Risk Management: It observes that ISO/IEC 42001 and the EU AI Act recognize, access, and mitigate AI-related risk. Thus, ISO/IEC 42001’s systematic approach helps organizations develop a process that aligns with the EU AI Act’s requirements. In this regard, following the ISO 42001 standard assists in creating a proactive approach to managing the AI-related risks that are critical components of the EU AI Act.
Ethical and Responsible AI Use: ISO 42001 encompasses AI’s ethical use and deployment, highlighting the principles of fairness, transparency, and accountability. Therefore, the principles are aligned with the key features of the EU AI Act. Thus, if your organization follows ISO 42001 standards, foster the ethical use of AI that helps implement the AI law.
Data Governance: The EU AI Act mandates strict data governance practices, especially for high-risk AI systems, to ensure data quality and minimize biases. ISO/IEC 42001’s guidelines on data management, including data quality, provenance, and preparation, can help organizations meet these requirements and promote the responsible use of data in AI systems.
Documentation and Reporting: Implementing ISO 42001 requires a comprehensive documentation process regarding policies, methods, and risks. This documentation can help execute the EU AI Act, as high-risk AI systems require extensive documentation and record-keeping.
Continuous Improvement: Both frameworks require constant monitoring and improvement for better AI management. In addition, the Plan-Do-Check-Act model in ISO 42001 helps improve the EU AI Act implementation process.
Transparency and Accountability: The ISO/IEC 42001 focus on openness and accountability in AI systems is consistent with the EU AI Act’s demand for clear and accessible information regarding AI system capabilities and decision-making processes. Compliance with ISO/IEC 42001 can assist enterprises in implementing the systems required to promote openness and accountability, which are fundamental to the EU AI Act.
Organizations generally require robust guidelines in AI management systems like the EU AI Act. Thus, implementing ISO 42001 denotes that the organization is committed to the ethical use of AI. The process maintains transparency, which is essential in the EU AI Act. Nevertheless, ISO/IEC 42001 compliance does not assure full EU AI Act compliance; it can be a valuable starting point for your organization to develop AI governance.
ISO 42001 AND THE EU AI ACT: A FRAMEWORK FOR TRUSTWORTHY AI
AI is growing and implemented across various industries, goods, and services. Therefore, AI is undoubtedly changing society and our lives and will continue to do so. Because of this advancement and impact, trust, ethics, and societal problems must be addressed. Further, AI must be dependable, equitable, transparent, and trustworthy. ISO/IEC 42001 specifies a certifiable AIMS framework for developing and deploying AI systems as part of an AI assurance ecosystem. The international standard outlines the requirements for creating, implementing, maintaining, and continuously enhancing an AIMS. The objective is to assist enterprises and society in reaping the maximum benefits from AI. It guarantees stakeholders that systems are being created and utilized appropriately.
The EU AI Act ensures that AI systems are continuously monitored and updated to avoid risks. If someone fails to define their use case accurately or ignores their responsibilities, they might face significant fines of up to EUR 40 million, or 7% of the firm’s global annual sales. This penalty is almost twice as severe as the worst penalties imposed for violations of the EU’s General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR). Thus, ISO/IEC 42001 is a recently issued ISO standard for developing, implementing, and maintaining AI systems. Hence, the standard is appropriate for organizations that provide AI-powered goods or services. Thus, the blog suggests that ISO 42001 can help follow the EU AI Act due to some common steps and objectives.
FAQ
What are the risks of the AI Act?
According to the EU AI Act, AI systems have four risk levels: unacceptable, high, limited, and minimal. Therefore, each risk has different regulations and requirements for organizations developing or using AI.
What are the unacceptable risks of the EU AI Act?
It explains the biometric identification and categorization of people, as well as the classification of people based on behavior, socio-economic status, or personal characteristics.
What is the EU AI Act prohibited?
The EU AI Act prohibits the manipulation or exploitation of people’s decisions and the evaluation or classification of people based on their social behavior or personal traits.
What other kinds of AI standards does ISO offer?
ISO /IEC 22989 defines AI terminology and describes the basic concept. Further, ISO/IEC 23053 creates an AI and machine learning (ML) framework for describing a generic AI system. Again, ISO/IEC 23894 offers guidance on risk management for AI-related organizations, reduces the risks, and maximizes the benefits.
What is the role of AI in management systems?
It automates repetitive tasks, saving time and increasing operational efficiency. It can also analyze large datasets and provide insights to support data-driven decision-making.

About the Author
ANUPAM SAHA
Anupam Saha, an accomplished Audit Team Leader, possesses expertise in implementing and managing standards across diverse domains. Serving as an ISO 27001 Lead Auditor, Anupam spearheads the establishment and optimization of robust information security frameworks.
IT COMPLIANCE IN 2024: ESSENTIAL TRENDS AND BEST PRACTICES
IT compliance is essential for every organization to secure the integrity and accountability of data. The process also helps develop the business and enhance its profitability. In today’s digital era, IT compliance has more than just a regulatory checkbox. It plays a...
POLICY MANAGEMENT SYSTEM: ESSENTIAL TOOLS FOR AUTOMATION AND SIMPLIFICATION
Growing businesses indicates that you become a master in your field and accurately manage all business-related policies. However, managing company policies can be daunting significantly when your business expands. Here, an effective policy management system can help...
NAVIGATING DATA PRIVACY FRAMEWORKS: A COMPREHENSIVE GUIDE
Globalization has intense effects on business functioning and scaling. In today's digital world, companies are generating an unprecedented rate of data that requires protection from emerging cyber threats. In addition, recurring data breaches and privacy concerns make...