ISO 27001 is an information security standard offering a robust framework. Thus, the standard helps implement and maintain an organization’s information security management system (ISMS). ISO published the standards in 1999, after which they underwent multiple revisions to improve their capabilities. The ISO 27001:2022 standard was upgraded in October 2022 to improve enterprise information security management. The most recent modifications occurred in 2013 and 2022.
This blog will discuss ISO 27001 2013 vs. 2022 and learn about the 27001 iso 2013 vs 2022 changes and how ISO 27001 is different between 2013 and 2022.
HISTORY OF ISO 27001 AND ISO 27002
COMPARING ISO 27001:2013 VS. 27001:2022:
CHANGES MADE IN THE ISO 27001 MANAGEMENT SYSTEM IN 2022
SUMMARY OF MAJOR CHANGES IN ISO 27001:2013 AND ISO 27001:2022
CHANGES MADE IN ANNEX A SECURITY CONTROLS:
CERTPRO OFFERS COMPREHENSIVE SUPPORT TO ACHIEVE ISO 27001 COMPLIANCE.
HISTORY OF ISO 27001 AND ISO 27002
ISO 27001 and ISO 27002 are both Information Security Management guidelines. Therefore, the first version of ISO 27001 came out in 2005 as an information security management system. It was first released in 1999 by the British Standard Institution (BSI). Therefore, the BS 7799-2 standard gives instructions on creating, using, managing, and improving an ISMS. After computer security became known worldwide, the ISO changed BS 7799-2 to ISO 27001 in 2005. ISO 27001 helps businesses strengthen their ISMS by explaining how to identify security risks, establish rules, and monitor system performance. In 2005, ISO/IEC 17799 changed to ISO/IEC 27002.
ISO 27002 provides a comprehensive list of best practices and regulations for computer security management. Additionally, it discusses many aspects of information security, such as managing assets, keeping employees safe, keeping the natural and environmental worlds safe, managing contacts and operations, and more. In addition, unlike ISO 27001, ISO 27002 is not legally binding. Instead, it helps companies pick and use the best security measures for their needs, risks, and legal and governmental needs. Both ISO 27001 and ISO 27002 provide recommendations on the choice and execution of information security measures, with ISO 27001 providing the criteria for creating an ISMS. Thus, ISO 27001 2013 vs 2022 standards give businesses a systematic way to manage information security and safeguard their priceless assets.
COMPARING ISO 27001:2013 vs. 27001:2022:
The ISO 27001:2013 VS. 27001:2022 helps you to understand the key differences:
Scope and Context: ISO 27001 2013 vs 2022 is an upgrade of the standard. ISO 27001:2022 has more reach than the previous standard. In addition, the broader range of coverage helps organizations better deal with new risks, like those related to cloud computing and AI. The current version also emphasizes understanding the company’s internal and external environment. This helps organizations tailor their security measures to their needs and situations.
Risk Assessment: The CIA triad (confidentiality, integrity, and availability) was the main focus of ISO 27001:2013’s risk assessment. ISO 27001:2022 takes a broader view. It informs the organization about physical protection, staff safety, and business continuity. This change makes it easier for companies to find and deal with risks in a broader range of situations, which makes them more resilient overall.
Leadership and Accountability: According to ISO 27001:2022, leaders must be involved and responsible in setting up and maintaining the ISMS. This increased participation of leaders is essential for building a strong security stance and making everyone feel responsible.
Control Objectives and Documentation: ISO 27001:2013 requires strict control goals and detailed documentation, while the latest version offers more freedom. Control goals are flexible and used in various organizational settings and risk levels. This lets organizations set priorities for their security efforts based on their needs. In the same way, documentation standards have been streamlined so that the focus is on actual applications rather than unnecessary documentation.
Performance Evaluation and Continual Improvement: The ISO 27001 revision shifts from periodic audits and reviews to continuous monitoring and evaluation. This change shows that security risks are constantly changing and that we need to be able to respond immediately. Organizations should always examine their security, find places to improve, and quickly take action to fix their problems. In the 2022 version, showing that you are always getting better is no longer a suggestion but a clear rule.
Communication and Stakeholder Engagement: ISO 27001:2022 stresses the importance of communication with partners, including clear reports on security performance. Stakeholders expect organizations to actively interact with them, asking for feedback and handling information security concerns. This open and honest communication builds trust among stakeholders and improves the organization’s image as a trustworthy keeper of information assets.
CHANGES MADE IN THE ISO 27001 MANAGEMENT SYSTEM IN 2022
ISO 27001 2013 vs 2022 has some specific changes. ISO 27001:2022 has the same number of clauses as ISO 27001:2013, but the text changes. The changes make ISO 27001 more like other ISO management standards. Thus, the changes primarily revolve around planning, defining process criteria, and monitoring standards.
1. Clause 4.2 Understanding the Needs and Expectations of Interested Parties: The subclause was added to analyze the requirements of the interested parties addressed in the ISMS process.
2. Clause 4.4 Information Security Management System: ISO 27001 2013 vs 2022 signifies that a new language requires organizations to identify necessary processes and their interactions within the ISMS. The ISMS must include the processes underpinning it, not just the ones specifically called out in the Standard.
3. Clause 6.2 Information Security Objectives and Planning to Achieve Them: This document now includes additional guidance on the information security objectives. Thus, it clarifies how objectives should be monitored regularly and formally documented.
4. Clause 6.3 Planning of Changes: The clause was added to standardize the planning. It states that changes to the ISMS shall be adequately planned if needed.
5. Clause 8.1 Operational Planning and Control: Further guidance was added for operational planning and control. Therefore, the ISMS needs to establish criteria for actions identified in Clause 6 and control those actions.
Additional minor changes include:
1. Clause 5.3 Organizational Roles, Responsibilities, and Authorities: Minor changes clarified that communication of roles relevant to information security are to be communicated within the organization.
2. Clause 7.4 Communication: Subclauses a-c remain the same; however, subclauses d and e have been simplified and combined into a new subclause d.
3. Clause 9.2 Internal Audit: The clause combined what existed between Clause 9.2.1 and 9.2.2 into one section.
4. Clause 9.3 Management Review: A new clause clarifies that the organization’s management review shall consider any changes.
5. Clause 10 Improvement: The clause now emphasizes continual improvement, nonconformity, and corrective actions.
SUMMARY OF MAJOR CHANGES IN ISO 27001 2013 vs 2022
It depends on the context and needs of the organization. The following is a summary of the advantages and disadvantages of ISO 27001 2013 vs 2022:
ISO-27001 2013: This version is the most widely used information security framework worldwide. Therefore, it has detailed and specific controls that offer guidance and assurance on your organization’s information security. Regardless, it is a complex and frigid framework that requires efforts to change the businesses and the environment.
ISO-27001 2022: The new version is more compatible and flexible. It offers customized services for different organizations. In addition, it has simple controls that reduce the cost of compliance and maintain consistency in the compliance process.
CHANGES MADE IN ANNEX A SECURITY CONTROLS:
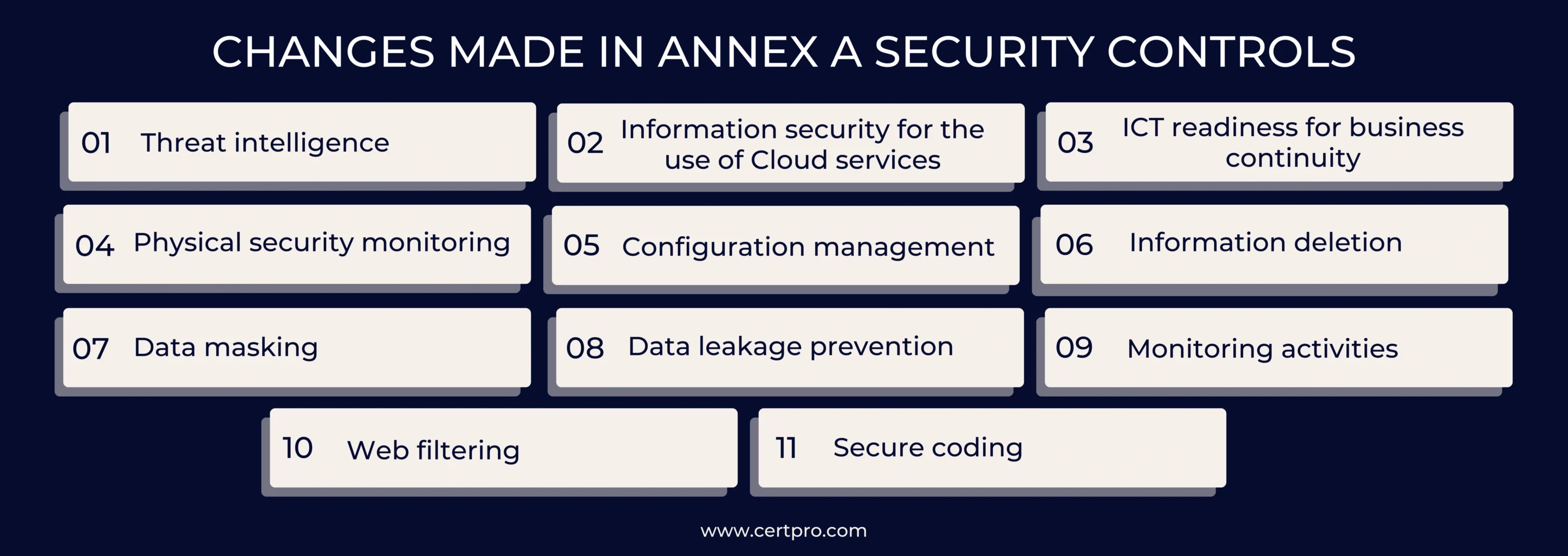
ISO 27001 2013 vs. 2022 signifies that eleven new rules were added to Annex A. If an organization is already certified under ISO 27001:2013, it must ensure it has the right processes to meet these new standards. If not, it must build new processes to add these controls to its existing ISMS. For example, “threat intelligence” means that businesses need to collect and study information about risks so they can take steps to lower risk. Companies certified under ISO 27001:2013 may not have implemented this component. It makes sense that threats are constantly changing, which is why this change is essential. This is related to a change made to ISO 27002 in 2022. ISO 27001 2013 vs 2022 can help make this straightforward because it has more information on how to adopt it.
Additionally, the new controls within ISO 27001:2022 contain:
A.5.7 Threat Intelligence: This control tells companies to gather and review information about risks to lower risk.
A.5.23 Information Security for the Use of Cloud Services: This control clearly shows that cloud information security needs improvement. It requires companies to set security standards for cloud services and have processes and procedures only used for them.
A.5.30 ICT Readiness for Business Continuity: Because of this control, businesses must ensure that their IT and communication systems can be used again after interruption.
A.7.4 Physical Security Monitoring: With this control, companies must monitor private areas like data centers, production facilities, and other places to ensure that only people can access them. This way, if there is a breach, the company will be aware of it.
A.8.9 Configuration Management: With this power, an organization must monitor how its technology is set up to ensure it stays safe and no one else can change it without permission.
A.8.10 Information Deletion: This control ensures that data is deleted when it is no longer needed, preventing the disclosure of private data and meeting privacy standards.
A.8.11 Data Masking: This control states that companies must use data filtering to keep private data safe, following their access control policy.
A.8.12 Data Leakage Prevention: Because of this power, businesses must keep private data from leaking out of systems, networks, and other devices.
A.8.16 Monitoring Activities: For this control to work, organizations must monitor their systems for strange activity and implement the right incident reaction processes.
A.8.23 Web Filtering: To protect IT systems, this control keeps companies track of which websites people visit.
A.8.28 Secure Coding: This control needs safe coding standards to be built into an organization’s software development process to lower security holes.
CertPro offers comprehensive support to achieve ISO 27001 compliance.
CertPro is a reputable partner that helps businesses successfully achieve ISO 27001 compliance. Thus, CertPro provides many beneficial services thanks to their knowledge and experience. We conduct in-depth gap analyses to pinpoint improvement areas and create specialized action plans. CertPro leads organizations through the implementation process while ensuring compliance with ISO 27001 requirements. We offer rigorous training and awareness initiatives to empower staff members and foster a security-conscious culture in ISO 27001 2013 vs 2022. Additionally, CertPro offers assistance with conducting risk analyses, setting up reliable information security procedures, and creating the relevant documentation. Through their thorough support, CertPro provides businesses with the resources and training necessary to achieve ISO 27001 compliance effectively.
FAQ
Are ISO 27001:2022's modifications major or minimal?
The key modifications to the standard are rather minor and may be rapidly adopted with minor changes to procedures and documentation. The controls in Annex A have undergone modest modifications, with some remaining the same, some getting new names, and a few new controls being introduced.
What separates ISO 27001:2022 from ISO 27001:2013?
The primary distinction is that ISO 27001:2022 places a greater focus on risk assessment and management. The revised edition incorporates criteria for supply chain security and gives firms more freedom to modify their information security management systems (ISMS).
Are the changes made to ISO 27001:2022 noteworthy?
While the majority of the standard has undergone relatively minor changes, the controls listed in Annex A have undergone more significant alterations, making them more obvious. Anyway, it is important to know about the changes made in ISO 27001:2022.
Is it necessary for organizations certified under ISO 27001:2013 to transition to ISO 27001:2022?
Indeed, it is important to be certified under the 2013 revision in order to preserve their certification. Firms accredited under ISO 27001:2013 must upgrade to ISO 27001:2022 before the end of their current certification period.
What new clauses are included in ISO 27001 2022?
The 2022 update to ISO 27001 contains a few minor adjustments to Clause 7.4. One may consider the adjustments to be a simplification. It eliminates the requirement to demonstrate the procedures by which communication will be carried out and replaces it with instructions on how to communicate.

About the Author
SUBBAIAH KU
Subbaiah Ku is the Regional Director for CertPro in Oman, bringing a wealth of expertise in process and system auditing. As a seasoned lead assessor, Subbaiah is dedicated to ensuring the highest standards in compliance and security. His unique blend of technical acumen, rooted in Mechanical Engineering, is complemented by a diverse range of certifications and extensive training.
HOW DOES ISO 27001 FOR STARTUPS IN INDIA HELP TO MEET GLOBAL STANDARDS?
India is the world’s fifth-largest economy, with a vibrant startup ecosystem that supports young professionals in making global changes. After the US and China, India ranks third globally for startup businesses. In this fascinating scenario, ISO 27001 for startups in...
IS SOC 2 THE SAME AS ISO 27001?
In today's digital landscape, ensuring the safeguarding of client data is paramount for businesses. Adhering to recognized compliance standards is vital to meeting this demand. ISO 27001 vs. SOC 2 represent two prominent benchmarks in the realm of data security with...
WHO NEEDS ISO 27001 CERTIFICATION AND WHY?
The esteemed ISO 27001 security framework is designed to evaluate the effectiveness of an organization's Information Security Management System (ISMS) in safeguarding its data. Obtaining ISO 27001 certification is a practical way for a corporation to demonstrate its...