ISO 27001 certification is an achievement for an organization seeking robust information security management. The standard is flexible to organizational demands and goals. In addition, ISO 27001 mandatory documentation recognizes which controls are needed for specific organizations. The core concept of the standard is to create ISO 27001 mandatory documents. Hence, documentation shows a clear auditable record of your commitment to ISO 27001.
In this context, the list of documentation is essential for the audit. However, auditors do not need to scrutinize everything. Still, your organization needs to document its controls and policies. In this article, we will discuss the ISO 27001 certification documentation requirements. We have shortlisted a few mandatory documents for ISO 27001 to help you on your certification journey.
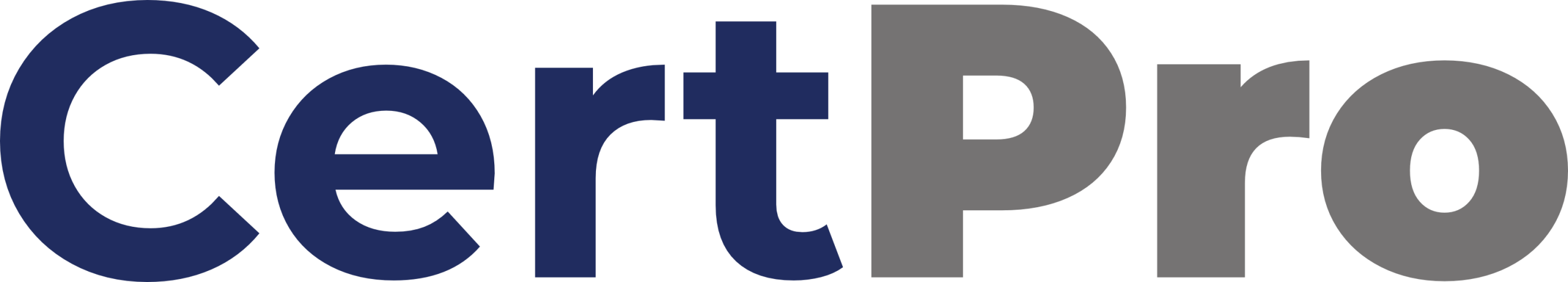
MANDATORY RECORDS OF ISO 27001
WHAT IS THE ISO 27001:2022 REVISION IMPACT ON MANDATORY DOCUMENTS AND RECORDS?
WHAT ARE THE MANDATORY DOCUMENTS OF ISO 27001?
HOW MANY MANDATORY CLAUSES ARE THERE IN ISO 27001?
WHAT ARE THE CONSEQUENCES OF MISSING ISO 27001 MANDATORY DOCUMENTS?
GET A PROFESSIONAL HELP FROM CERTPRO
MANDATORY ISO 27001 DOCUMENTS
The ISO 27001 mandatory documents list is not an official contract for the standard. However, based on our experiences and knowledge, we share which documents are essential for certification.
Scope of the ISMS: This lets your business’s stakeholders know exactly what parts your ISMS covers. In addition, it includes a mission statement and plans with your ISMS scope to help your stakeholders understand. Thus, your written ISMS scope is essential to getting certified.
Information Security Policy and Objectives: The organization’s top leaders must create an information security strategy that fits your needs. Hence, the policy shows that top management is dedicated to improving the ISMS goals.
Risk Assessment and Treatment: Explain how you identify, analyze, evaluate, and prioritize your organization’s risks. Choose what works for your business and create a report showing how your risks are managed.
Statement of Applicability: An SOA is the key link between determining and treating risk. It is a controlled document that is constantly updated and explains how information security is implemented.
Risk Mitigation Plan: 6.1.3 says what you must do to make a risk treatment plan. Simply explain how you will handle information risks and show that your chosen method works well.
Risk Assessment Report: Once you know the risks, you must determine which ones need more attention and how those tests are initiated. A broad assessment of the information security risk should be conducted at least once a year.
Definition of Security Roles and Responsibilities: Security involves ensuring that everyone or every group in a company knows their roles and responsibilities and who is responsible for what when it comes to information security. Thus, this helps everyone work together and ensures that security-related tasks do not overlap.
Inventory of Assets: Organizations can better understand their assets by making an inventory. A business names and lists all its information assets in an inventory of assets. Thus, this list also includes physical assets such as hardware, software, data repositories, intellectual property, private information, and sensitive data.
Acceptable Use of Assets: Rules about who can use your company’s IT tools and how to use them are essential. Anyone, like contractors and temp workers, should be able to see the rules for how to use your IT assets.
Access Control Policy: It is a great idea to have both a general access control policy and specific limited access guidelines about things like passwords, firewalls, VPNs, and so on.
Operating Procedures for IT Management: IT and security procedures include standards and best practices for handling and running safe IT systems. These steps cover managing changes, controlling access, being aware of security holes, applying patches, and responding to incidents.
Secure System Engineering Principles: It is possible to avoid problems with Control 8.27. Thus, it ensures that you get rid of CIA threats. Protecting the privacy, integrity, and accessibility of your data is crucial.
Supplier Management Policy: You control almost everything that occurs inside your organization. However, you can not control the safety of your providers, so ensure they have their own protection rules.
Incident Management Procedure: According to ISO 27001, a security incident is an unwanted event that risks the privacy, integrity, or availability of information. As with all things ISO, dealing with an incident should include quickly gathering proof, doing forensic analysis, telling people about the incident, and keeping records. This is true whether it’s a hacking attack or a computer system breach.
Business Continuity Procedures: No matter how threatening a security incident or event is for your business, you need to be able to keep doing the necessary things and keep working toward approval. Again, Business Continuity Management relates to disaster management and should be documented in policies, plans, processes, reports, and strategies.
Statutory, Regulatory, and Contractual Requirements: Annex A.18.1 is the tricky part of ISO-compliant. People who work for businesses need to realize how many laws and rules affect them. However, your cooperative auditor wants to know how you’ve met your legal, regulatory, and contractual duties.
MANDATORY RECORDS OF ISO 27001
The ISO 27001 mandatory documents are:
Records of Training: Managing an ISMS is not accessible. Your team needs many skills and training, not just security. To demonstrate compliance, you can quickly create a table showing who’s involved, what they do, and their experience.
Monitoring and Measurement Results: Monitoring means watching data made by a process or a system. Thus, you need to gather data for auditing. For example, you could monitor the availability of your website by checking the uptime percentage. In addition, you can measure the availability by counting how many server crash reports arise in your ticketing system.
Internal Audit Program: It was already said that you need an internal audit, and you must do it often to ensure that your ISMS keeps up with ISO 27001 standards.
Results of Internal Audits: It is crucial to record internal audit reports. In addition, it must have documentation review, evidence, interviews with the staff, and assessment findings.
Results of the Management Review: A management review aims to inform top management and prove that the adopted ISMS and its goals are still functional, honest, and open.
Results of Corrective Actions: As soon as a risk is recognized, steps must be taken to fix it. In this regard, document the problem and fix the process.
Logs of User Activities: When you log actions, exceptions, and events, remember that private, sensitive, or personal information could be used. This is why you need to ensure protection measures are in place.
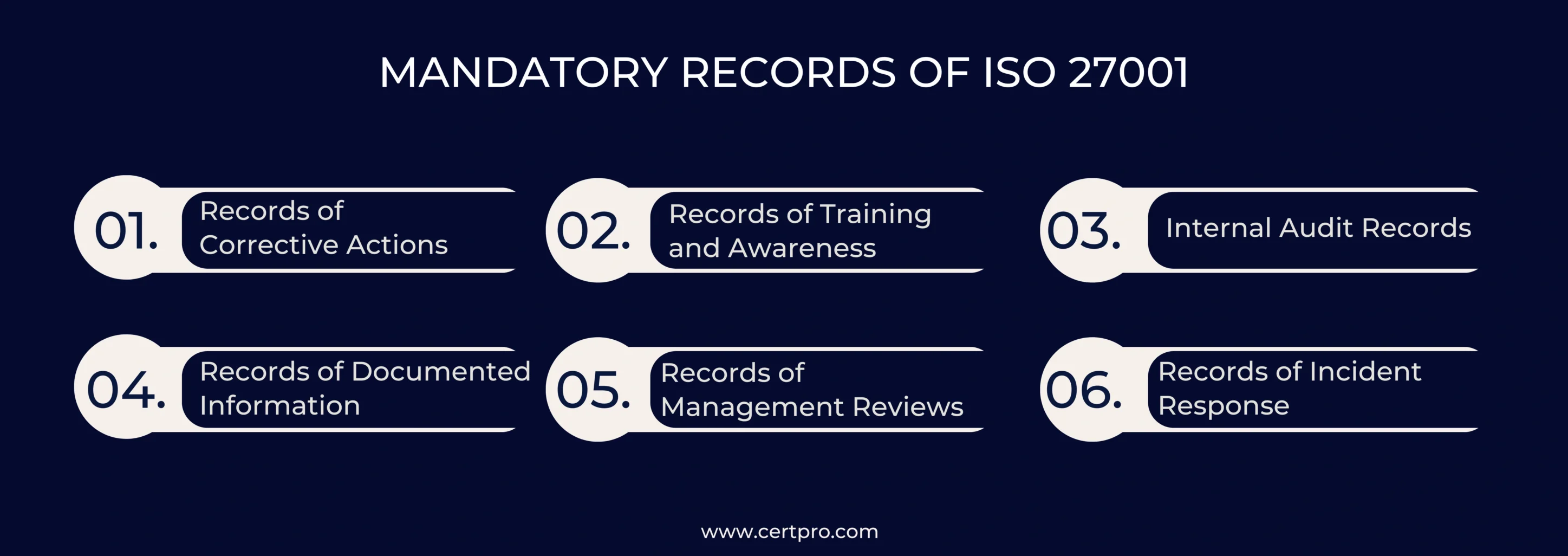
WHAT IS THE ISO 27001:2022 REVISION IMPACT ON MANDATORY DOCUMENTS AND RECORDS?
The ISO 27001 2022 revision updates and adjustments to the ISO 27001 mandatory document requirements. It affects the obligatory papers and records. Here are some broad points to keep in mind, even if the precise adjustments may vary:
Examine and Update: In light of the updated ISO 27001 standards, organizations must examine their current obligatory documentation and records. This helps determine gaps that are modified to comply with the new standard.
Documents Introduced Newly or Modified: The revision may call for adding new, mandatory documents or revising existing ones. The documentation for an organization’s information security management system (ISMS) should include any newly necessary papers.
Enhanced Documentation Requirements: The amended standard could give some parts of documentation more prominence. Organizations need to submit information to demonstrate their compliance.
Streamlining and Simplification: The adjustment may make the documentation requirements more efficient and straightforward. This can entail reducing the number of required papers or changing their format. It makes them more transparent and easier to understand.
Alignment with Annex A: The 2022 version may modify Annex A, which contains a summary of the control goals and controls. Organizations must thus check their Statement of Applicability (SoA) and related documents to ensure they accurately represent the most recent control needs.
Transition Period: Organizations that have previously achieved the ISO 27001 required documents will probably have a transition period to modify their paperwork to comply with the new standards. It is crucial to remain current on accreditation or certification agencies’ transitional instructions.
WHAT ARE THE MANDATORY DOCUMENTS OF ISO 27001?
The ISO 27001 requirements rules list the most essential parts of a company’s cybersecurity plan. Although there isn’t a formal list of ISO 27001 mandatory documents that must be submitted, a standard set of six configurations meets all of ISO 27001’s clauses.
1. Scope of the ISMS Document: The short ISMS Scope Document lists the assets and areas your plan should safeguard from threats. This list of parts that could be vulnerable defines the scope of the entire security plan and is an essential first step.
2. Information Security Policy: Senior management is in charge of making a complete security policy that fits that specific company’s needs and ways of doing business. This strategy must be backed up by proof that everyone in the company knows about and follows the suggested steps. Clients and partners may want to read and assess this policy, so it is essential to ensure it is complete, detailed, and robust. Therefore, give weight to exact facts and provide clear, measurable steps instead of depending only on vague promises.
3. Risk Assessment and Methods: The risk assessment and methodology report is one of the most research-intensive documents required by ISO 27001. For example, when determining the risk of company-issued laptops, it is essential to consider the number of laptops in use, the type of laptops, and the security settings on each computer.
4. The Application’s Statement: The applicability of the 114 extra security measures included in ISO 27001’s Annex A varies by company type. For example, one requirement in Annex A is that IT personnel have Non-Disclosure Agreements (NDAs); nevertheless, this may not apply to firms without IT personnel.
5. Plan for Risk Treatment: This plan meets ISO 27001 mandatory documents by giving you four ways to reduce risks: changing the risk, ignoring it, sharing it, or saving it. The focus is on specific plans for essential problems. By filling out this risk treatment plan, you help auditors check for compliance and success while strengthening security methods. These plans need to be very specific to promise a solid response to possible security risks.
6. Security Objectives: This section lists an organization’s cybersecurity objectives and the previously established risk assessment and remediation procedures. Before compiling the necessary ISO 27001 mandatory documents, many firms may already have existing goals, and it is best to include both current projects and future ambitions.
These objectives should be concrete and measurable, emphasizing practical advantages rather than just administrative aspects. Again, auditors will look for evidence of the active pursuit of these aims and tangible outcomes. For example, if the goal is to maintain a dependable cloud service, giving data on the service’s total uptime and downtime is critical. Another measurable goal may be for employees to recognize and report phishing emails to security personnel.
HOW MANY MANDATORY CLAUSES ARE THERE IN ISO 27001?
ISO 27001 comprises two sections: Mandatory Clauses and Annex A Controls.
1. Mandatory Clauses: The first part of the ISO 27001 standard comprises 11 clauses (0–10), of which clauses 4–10 are the ones a business needs to execute to comply with ISO 27001 standards.
2. Annex A Controls: The latest ISO 27001 version includes 93 security controls from which an organization can develop its security risk assessment.
WHAT ARE THE CONSEQUENCES OF MISSING ISO 27001 MANDATORY DOCUMENTS?
During an audit for ISO 27001 certification, an auditor records major and minor nonconformities and areas for improvement. The lack of ISO 27001 mandatory documents. It is integral to a major nonconformity. Therefore, these non-conformities can slow down the certification process. Thus, proper ISO 27001 mandatory documents need to be incorporated. You must find or make the necessary proof to fill in the blanks and fix these issues. Hence, depending on how long it takes to gather and show the evidence, this process may give you an extra one to four weeks to meet your deadline.
Get a professional help from CertPro
To comply with ISO 27001, organizations must create and keep several essential papers. These documents are the basis of a sound information security management system and give you a way to find, evaluate, and handle threats to information security. In this regard, CertPro is a trustworthy company that knows much about ISO 27001 mandatory documents. Thus, we can help businesses with the certification process.
Furthermore, Companies can get help, advice, and tracking services from CertPro to ensure the ISO 27001 27001 mandatory documents. Businesses work with CertPro to safeguard private information and valuable assets. Thus, it helps to boost their information security and gain the trust of their stakeholders.
FAQ
What information must the ISMS documentation have?
How many provisions of ISO 27001 need to be followed?
The two components of ISO 27001 are organized separately. 11 clauses make up the first and most important section, from clause 0 to clause 10. The foundation for your Statement of Applicability (SoA), comprising 114 controls, is provided in the second portion, Annex A.
What are the six ISO-required procedures?
What are the requirements for passing ISO 27001?
Who conducts audits of ISO 27001?
Auditors who are qualified and impartial must conduct audits in accordance with ISO 27001. It is often necessary for the auditor to demonstrate competence for an ISO 27001 audit by having a proven understanding of the standard and auditing best practices.

About the Author
SUBBAIAH KU
Subbaiah Ku is the Regional Director for CertPro in Oman, bringing a wealth of expertise in process and system auditing. As a seasoned lead assessor, Subbaiah is dedicated to ensuring the highest standards in compliance and security. His unique blend of technical acumen, rooted in Mechanical Engineering, is complemented by a diverse range of certifications and extensive training.
IS SOC 2 THE SAME AS ISO 27001?
In today's digital landscape, ensuring the safeguarding of client data is paramount for businesses. Adhering to recognized compliance standards is vital to meeting this demand. ISO 27001 vs. SOC 2 represent two prominent benchmarks in the realm of data security with...
IS ISO 27001 RISK ASSESSMENT VITAL FOR SECURITY MEASURES?
The ISO 27001 standard provides a framework for information security, highlighting the importance of a thorough risk assessment procedure. Organizations use the methodical and complex ISO 27001 risk assessment process to identify and assess information security...
ISO 27001 COMPLIANCE REPORT
The protection of sensitive information has become critical for businesses and organizations in today's digital age. With the rising frequency and sophistication of cyber threats, it is critical to implement strong security measures to safeguard critical data. ISO...